Common-mode noise voltage pulses from AC-DC chargers can affect the signal reception of capacitive panels during charging, which may lead to inaccurate touch readings or false touch signals. This has prompted cell phone manufacturers and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) to jointly develop the IEC 62684 Standard to harmonize charger interfaces. Charger manufacturers are looking for fast and stable solutions for production testing and common-mode noise measurement to ensure that the electrical and electromagnetic interference characteristics of each product meet these standards. The IEC62684 not only regulates USB cable and connector specifications and reliability (frequency of use) requirements, but also defines requirements to input/output voltage and current range tests, protection tests, etc. The required items are as follows:
- 5.1 DC plug connector specifications
- 5.2 AC input characteristics
- 5.4 DC output characteristics
- 5.5 (Short circuit) protection test
- 5.6 EPS detection
- 5.7 Reliability (frequency of use)
- 6.2 DC output common-mode voltage detection
- 6.3 DC output ripple voltage detection
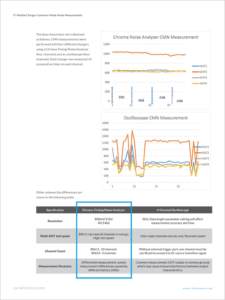
Since the common-mode voltage test method described in IEC62684 6.2 is not suitable for high-volume automated test applications, the EN301 489-1 MoU provides a new test method and defines common-mode noise components, specification limits and measurement setup recommendations for mobile device chargers. After extensive verification testing and fine-tuning, Chroma has realized automatic testing of charger common-mode noise with the Chroma 8000/8020 ATE. An easy-to-understand table allows users to set relevant test parameters for fast and stable common-mode noise measurements. Complemented by their ability to complete common-mode noise measurements of 4 DUTs at a time in as little as 2 seconds, these systems are well suited to meet the needs of high-speed and high-volume production line testing.
This paper offers an overview of the requirements of the IEC62684 Standard, related test equipment, systematic and automated test, and provides suggestions based on our extensive experience with measuring charger common-mode noise. We hope this paper provides test engineers with a more comprehensive understanding of charger common-mode noise and leaves them better equipped to perform related tests and measurements.