As electric vehicle (EV) technology advances, the on-board charger (OBC) has become a core module integrating power electronics and vehicle communications. Because architectures and protocols vary by OEM, test systems face varied and demanding requirements, especially in terms of real-time responsiveness and protocol handling.
Startup timing verification requirements:
In most vehicle platforms, once the system powers up, the OBC must receive and parse multiple critical CAN messages within 200–600ms to determine whether startup conditions are satisfied. Because response windows and message sequences vary by OEM, the test system needs fine-grained timing control and real-time data feedback to support this verification effectively.

Differences in message forwarding logic during charging:
In some vehicle architectures, the OBC not only handles charging control messages from the EVSE but also acts as a CAN gateway for DC fast charging, translating CAN frames and rebroadcasting them within 10ms to other control modules on the vehicle’s CAN buses (e.g., the battery management system, BMS, or the vehicle control unit, VCU). Requirements can vary by model for message-ID mapping, data encapsulation, and even transmit/acknowledgment schemes. The test platform must therefore support high-speed communications as well as real-time emulation of the relevant controller models to verify overall correctness and stability.
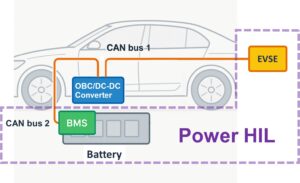
Beyond reproducing real AC/DC high-power input/output behavior, the Chroma 8620 OBC/DC-DC Power HIL (Hardware-in-the-Loop) System delivers high-speed processing and real-time protocol handling. It accurately simulates message transmission and reception during the startup sequence, and provides comprehensive communication logs and timing-analysis tools to help engineers confirm that handshakes and state transitions complete within the expected time. While supporting a wide range of CAN communication tests, the Power HIL system can also integrate models of the EVSE, BMS, and other in-vehicle controllers to build a realistic, easily reproducible test environment. With dynamic power emulation and injection of faults and abnormal conditions, it enables further validation of OBC behavior and stability across operating scenarios.
The Chroma 8620 has been successfully used by multiple automotive customers to perform the timing verification and gateway functionality tests described above. The system helps engineering teams shorten test cycles and boost verification efficiency, and its real-time fault injection capability mitigates potential timing errors and communication risks in early development. This approach aligns with the functional safety principles of ISO 26262 and strengthens product reliability ahead of vehicle-level integration.

